Maximum Visibility Facility Selection in Spatial Databases
Keywords: Computational Geometry, Spatial Databases, R-Tree, Graph Partitioning, Integer Program Optimization.
In this project, I worked extensively on the Maximum Visibility Facility Selection (MVFS) problem. I used tools from computational geometry, graph theory, and spatial databases to efficiently process the MVFS query.
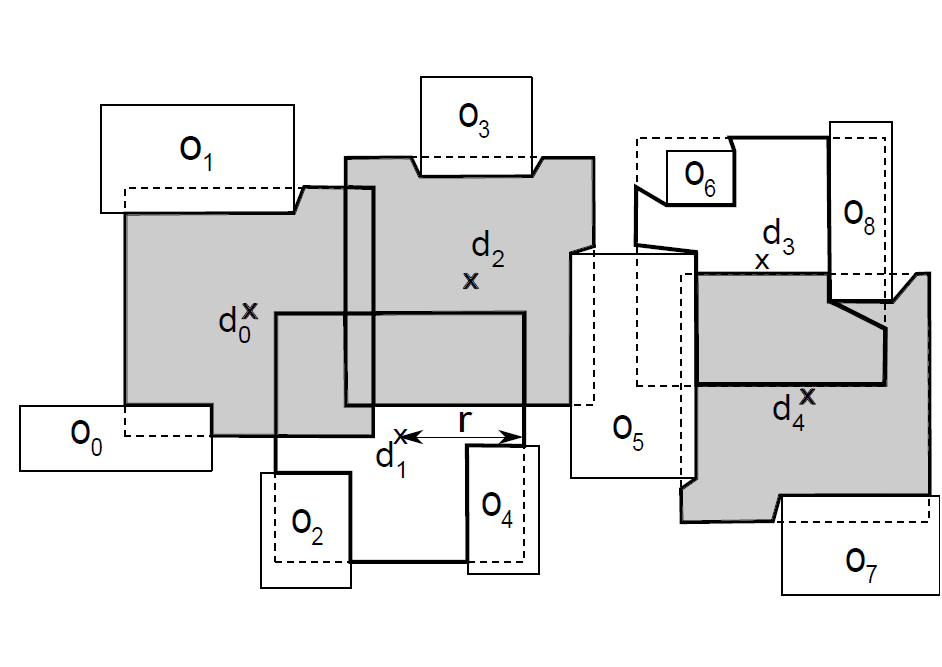
In the MVFS problem, we are given a large set of obstacles in 2D or 3D space, a set of n candidate locations where facilities can be established. The MVFS query finds k out of the n locations, that yield the maximum visibility coverage of the data space. A sample instance of the MVFS problem with n=5 and k=3 is shown in the figure above.
Though the MVFS problem has been extensively studied in visual sensor networks, computational geometry, and computer vision in the form of the optimal camera placement problem, existing solutions are designed for discretized space and only work for MVFS instances having a few hundred facilities. To this end, we introduce the concept of equivisibility triangulation to devise the first approach to accurately determine the visibility coverage of continuous data space from a subset of the facility locations, which avoids the limitations of discretizing the data space. Then, we propose an efficient graph-theoretic approach that exploits the idea of vertex separators for an efficient exact in-memory solution to the MVFS problem. Finally, we propose the first external-memory approximation algorithm that is scalable for a large number of obstacles and facility locations. We conduct an extensive experimental study to show the effectiveness and efficiency of our proposed algorithms. The source code for this project can be found in this Github repository.
Publications
- Md Ishat-E-Rabban, Mohammed Eunus Ali, Muhammad Aamir Cheema, Tanzima Hashem, The Maximum Visibility Facility Selection Query in Spatial Databases, Proceedings of the 27th ACM SIGSPATIAL, 2019. paper
