Resilient Multi-Robot Task Optimization
Keywords: Greedy Algorithm, Local Search, Coverage Maximization, Persistent Monitoring.
Source Code: Github
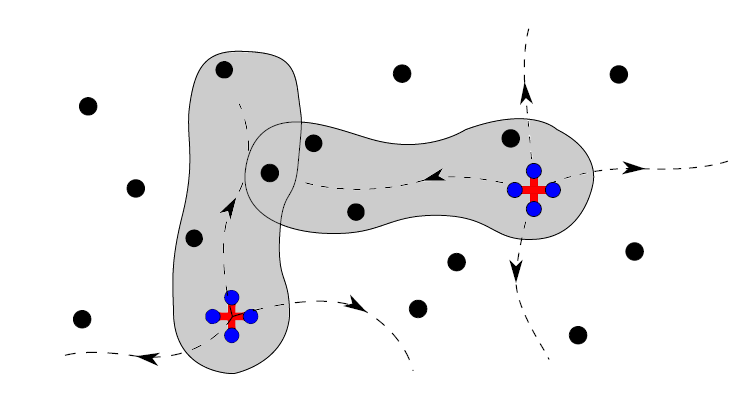
In this project, I study multi-robot task optimization while taking into account the resilience of the system. I explore two multi-robot tasks: coverage maximization and persistent monitoring. In the coverage maximization task, a team of robots aims to cover a set of targets. For each robot, there is a set of candidate trajectories, one of which the robot will follow. The list of targets covered by each robot trajectory is provided. It is assumed that at most α robots may fail, but it is unknown which robots are going to fail. The objective of the problem is to select one trajectory for each robot such that the target coverage is maximized in the case of a worst-case failure of α robots. We call this problem the Resilient Coverage Maximization (RCM) problem. The RCM problem is known to be NP-hard. A sample instance of the RCM problem is shown in the following figure.
I have proposed two algorithms for the RCM problem that outperform the only existing algorithm, called 2PG, both in terms of accuracy and running time. Here, by the accuracy of a solution, we mean how much target coverage the solution achieves with respect to an optimal solution. Our proposed algorithms are called the Ordered Greedy (OrG) algorithm and the Local Search (LS) algorithm. The OrG algorithm produces an ordering of the robots according to some sorting criteria, and greedily selects the trajectories of each robot sequentially according to the sorted order such that, for each robot, the marginal increase in target coverage is maximized. Experimental results show that the accuracy of the OrG algorithm is slightly better than the 2PG algorithm, and it runs significantly faster than the 2PG algorithm.
In the LS algorithm, we start with an initial solution to the RCM problem. Then, in each iteration, we consider a set of neighbors (to be defined later) of the current solution, estimate the accuracy of the neighbors, and select the neighbor with the highest estimated accuracy. The algorithm terminates when we find a local optima. Empirical studies show that the accuracy of the LS algorithm is significantly better than the 2PG algorithm, while the two algorithms are close to each other in terms of running time.
I also test the performance of the proposed algorithm in a simulated environment using a case study. The case study is based on the multi-robot persistent monitoring task. I select trajectories of the robots such that target coverage is maximized in case of a worst-case failure of $\alpha$ robots. The simulation of the case-study environment, rendered using OpenGL, is shown at the top of this page.
Publications
Md Ishat-E-Rabban, Pratap Tokekar, Failure-Resilient Coverage Maximization With Multiple Robots, IEEE Robotics and Automation Letters, volume 6, Issue 2, 2021. paper
Md Ishat-E-Rabban, Pratap Tokekar, Improved Resilient Coverage Maximization with Multiple Robots, Workshop on Heterogeneous Multi-Robot Task Allocation and Coordination at Robotics: Science and Systems, 2020. paper
